A new system of government was put in place and the Persian multi-national state was developed.
As Cyrus vowed in his cylinder to respect the people of Babylon, and since he liberated the incarcerated Jews to be returned to their homeland, he was viewed as the legitimate successor of the ancient Babylonian kings and became popular in Babylon itself, in contrast to Nabonidus. Please refer to the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have any questions. In this distress either some one made the suggestion to him, or he bethought himself of a plan, which he proceeded to put in execution. The Babylonian Chronicle records that Babylon was captured on 16th Tartu, which was the night before the akitu festival in honor of Sin, the moon god.[26]. [citation needed], Nabonidus and Belshazzar's Assyrian heritage is also likely to have added to this resentment. On the sons committing suicide in captivity, his mother swore revenge and defeated and killed Cyrus. This system of government reached its peak after the conquest of Egypt by Cambyses II during the reign of Darius I, thereafter receiving its ideological foundation in the inscription of the Persian kings.
It has long been maintained that the foundation of Seleucia diverted the population to the new capital of Babylonia, and that the ruins of the old city became a quarry for the builders of the new seat of government, but the recent publication of the Babylonian Chronicles of the Hellenistic Period has shown that urban life was still very much the same well into the Parthian age (150 BCE to 226 CE). Even so, its highly significant that he thought it important to promote himself as an enlightened despot to the world at large. So imagine youre one of those Mesopotamians, formerly subject to the Babylonians, who are now receiving back your gods. He became the epitome of the great qualities expected of a ruler in antiquity, and he assumed heroic features as a conqueror who was tolerant and magnanimous as well as brave and daring. He seemed to have left the defense of his kingdom to Belshazzar (a capable soldier but poor diplomat who alienated the political elite), while occupying himself with the more congenial work, like excavating foundation records of the temples and determining the dates of their builders. When Cyrus reached this stream, which could only be passed in boats, one of the sacred white horses accompanying his march, full of spirit and high mettle, walked into the water, and tried to cross by himself; but the current seized him, swept him along with it, and drowned him in its depths. Little is known of the family life of Cyrus. And thus, making their way by the quickest route, they soon found themselves before the kings palace.
It does, however, indicate the high esteem in which Cyrus was held, not only by his own people, the Persians, but by the Greeks and others. In the 4th century BCE, Xenophon wrote a biography that framed Cyrus as the ideal ruler; Ctesias also wrote about Cyruss life in the 4th century, offering an account that diverges notably from Herodotuss. Please select which sections you would like to print: What ancient sources mention Cyrus the Great?
Permission to do so was embodied in a proclamation, whereby the conqueror endeavored to justify his claim to the Babylonian throne. A battle was fought at a short distance from the city, in which the Babylonians were defeated by the Persian king, whereupon they withdrew within their defenses. However, you dont have to travel to London to see what it looks like. Several revolts of the Greek cities were later suppressed with severity. [4] To the east, the Achaemenid Empire had been growing in strength. He merely wanted to represent himself to the world as merciful in victory. Besides youve managed to preserve your Jewish religion and your Jewish traditions, and things can only get better now that the Persians are in chargeright? a stream which, rising in the Matienian mountains,runs through the country of the Dardanians, and empties itself into the river Tigris. This may be the source of the story by Herodotus that the Persian army, having diverted the Euphrates, entered Babylon along the riverbed.
[24], Gauthier Tolini has proposed a plausible reconstruction of how Babylon fell. Thats how it appears on contemporary maps made on clay tablets. Cyruss career as a military leader began in earnest in 550 BCE, when he rose up against his Median overlord (and by some accounts, his grandfather), King Astyages. All rights reserved.
According to the Greek historian, Cyrus was at first successful in defeating the ruler of the nomadscalled the Massagetaiwho was a woman, and captured her son. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content.
An account of the latter appears in the Bible: Cyrus is the ruler that liberated the Jewish people from their Babylonian captors. Babylon has a seven-story ziggurat dedicated to Mardukwe met ziggurats in the lecture on being Mesopotamian, they resemble step or terraced pyramidsthis one is known as Etemenanki, The Foundation of Heaven and Earth.. The meaning of his name is in dispute, for it is not known whether it was a personal name or a throne name given to him when he became a ruler. 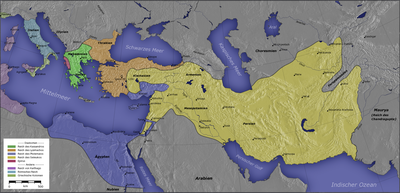
The conquest was quick, for even the priests of Marduk, the national deity of the great metropolis of Babylon, had become estranged from Nabonidus. Those who opposed the forces under Gobryas were struck down, including those outside the banquet hall. When Cyrus defeated Astyages he also inherited Median possessions in eastern Iran, but he had to engage in much warfare to consolidate his rule in this region. But Cyrus was not only a great conqueror and administrator; he held a place in the minds of the Persian people similar to that of Romulus and Remus in Rome or Moses for the Israelites. For good measure, Nebuchadnezzar had also put out the eyes of their king Zedekiah and destroyed Jerusalem.
He then sees a hand writing on the palace wall. In short, the figure of Cyrus has survived throughout history as more than a great man who founded an empire. Herodotus, although writing long after the events, had traveled in Mesopotamia and spoken to Babylonians. Cyrus also tells us that he returned all the statues of the gods, which Nabonidus had filched from other cities in Mesopotamia, to their rightful templesto the places that make them happy, as he touchingly expresses it.
Such, then, were the circumstances of the first taking of Babylon. He conciliated local populations by supporting local customs and even sacrificing to local deities. Babylonia was thereafter incorporated into the Persian Achaemenid realm as a satrapy. In October 539 BCE, Cyrus the Great entered Babylonia in peace without being engaged in any battle. Here they shut themselves up, and made light of his siege, having laid in a store of provisions for many years in preparation against this attack; for when they saw Cyrus conquering nation after nation, they were convinced that he would never stop, and that their turn would come at last.
It is also possible that stories about Cyrus were told (and embellished) by Persian court society and that these are the basis of Xenophon's text. Accordingly he put off for a time his attack on Babylon, and, dividing his army into two parts, he marked out by ropes one hundred and eighty trenches on each side of the Gyndes, leading off from it in all directions, and setting his army to dig, some on one side of the river, some on the other, he accomplished his threat by the aid of so great a number of hands, but not without losing thereby the whole summer season. Historians also use the term Liberation of Babylonia interchangeably.
Cyrus claimed that Marduk deserted the Babylonians because Nabonidus had reduced the citizenry to servile status. In 539 BCE, Cyrus invaded Babylonia. The document in question was written on a clay cylinder, called the Cyrus Cylinder inscribed in Babylonian cuneiform. After his conquest of Babylonia, he again turned to the east, and Herodotus tells of his campaign against nomads living east of the Caspian Sea. So that was the end of the Egyptian empire, and the beginning of the Persian supremacy. [17] Modern scholarship[18][19][20][21] recognizes the Cyrus Cylinder as a propaganda tablet designed to manipulate the public against Nabonidus and to legitimize Cyrus' conquest of Babylon. In the year 1971, Iran celebrated the 2,500th anniversary of the founding of the monarchy by Cyrus.
The Book of Daniel (2nd century BCE), chapter 5 relates the final night of Belshazzar, just before the Persian invasion. The account of the Fall of Babylon - which is here presented in the translation by George Rawlinson - proves beyond all reasonable doubt that the author never talked to a Babylonian about the event and never visited the city. In October 539 bce, the greatest city of the ancient world fell to the Persians. The Cyrus Cylinder is permanently housed in the British Museum.
There is no doubt that the Cyrus saga arose early among the Persians and was known to the Greeks. In the cylinder the king of the world, as Cyrus pompously called himself, describes how he conquered Babylon in 539 B.C.without a fight, or so he allegesand then took its king, Nabonidus, prisoner, all with the aid of Marduk. This page was created in 1996; last modified on 14 July 2020. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article (requires login). Cyrus, enraged at the insolence of the river, threatened so to break its strength that in future even women should cross it easily without wetting their knees. His chief adviser, however, instead gave the baby to a shepherd to raise. Babylon is a very international city, because merchants and tourists throng to it from all around. [8] Nabonidus surrendered and was deported. In the Bible (e.g., Ezra 1:14), Cyrus is famous for freeing the Jewish captives in Babylonia and allowing them to return to their homeland. Hereupon the Persians who had been left for the purpose at Babylon by the, river-side, entered the stream, which had now sunk so as to reach about midway up a man's thigh, and thus got into the town. The Cyropaedia (4.6.3) states that a father and son were both reigning over Babylon when the city fell, and that the younger ruler was killed. A receipt for reconstruction work on the Enlil Gate demonstrates that there was a forced entry into Babylon. [9] Although the Jews never rebelled against the Persian occupation,[10] they were restive under the period of Darius I consolidating his rule,[11] and under Artaxerxes I,[12][13] without taking up arms, or reprisals being exacted from the Persian government. And if you had been one of themone of the few who did return you would no doubt have felt extremely emotional, particularly if you had been one of the very few original Jewish exiles who were still alive after 48 years. He also spent time outside Babylonia, rebuilding temples in the Assyrian city of Harran, and also among his Arab subjects in the deserts to the south of Mesopotamia. In any case, it is clear that Cyrus came from a long line of ruling chiefs. His reputation as great was probably enhanced by the extent to which his figure was mythologized. Corrections? Cyrus was born between 590 and 580 bce, either in Media or, more probably, in Persis, the modern Frs province of Iran.
The ruins today, though few, arouse admiration in the visitor.
Babylonia had always been more vulnerable to conquest and invasion than its northern neighbour, and without the might of Assyria to keep foreign powers in check, Babylonia was ultimately exposed. According to Xenophon, Belshazzar was killed in this conflict, but his account is not widely accepted. Cyrus the Great, also called Cyrus II, (born 590580 bce, Media, or Persis [now in Iran]died c. 529, Asia), conqueror who founded the Achaemenian empire, centred on Persia and comprising the Near East from the Aegean Sea eastward to the Indus River. In October 539 BCE, the Persian king Cyrus took Babylon, the ancient capital of an empire covering modern Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, and Israel. Croesus, king of Lydia in Asia Minor (Anatolia), had enlarged his domains at the expense of the Medes when he heard of the fall of Astyages, and Cyrus, as successor of the Median king, marched against Lydia. Cyrus the Great was the founder of the Achaemenian Empire. So lets now leave the Persians for a moment and suppose youre a Jew living in Babylon.
Learn more aboutAkkadian Empire arts and gods. [32] Deutero-Isaiah's predictions of the imminent fall of Babylon and his glorification of Cyrus as the deliverer of Israel date his prophecies to 550539 BCE, and probably towards the end of this period.[33]. Herodotuss story may be apocryphal, but Cyruss conquests in Central Asia were probably genuine, since a city in farthest Sogdiana was called Cyreschata, or Cyropolis, by the Greeks, which seems to prove the extent of his Eastern conquests. [2] This surprise capture of Babylon is consistent with the story recorded in Daniel 5. Babylon is a spectacular and bustling city. Gobryas was then made governor of the province of Babylon. Astyages tries to forestall the events of the dream but instead brings them to fruition. So, in sum the Persian Empire was anything but hostile to its Jewish population, and the Jews for their part have never forgotten Cyrus generosity. Updates? The Histories by the Greek researcher Herodotus of Halicarnassus (fifth century BCE) are the world's first historical study.
FROM THE LECTURE SERIES: THE OTHER SIDE OF HISTORY: DAILY LIFE IN THE ANCIENT WORLD, December 2, 2020
Babylonia The sack of Babylon and ancient Near East chronology, Learn how and when to remove this template message, Translation is that of Henry Graham Dakyns, available online, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Fall_of_Babylon&oldid=1089704004, Military history of the Achaemenid Empire, Articles with unsourced statements from March 2021, Articles needing additional references from March 2021, All articles needing additional references, Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0, This page was last edited on 25 May 2022, at 06:00. He said that he didnt allow his troops to commit any atrocities when he took the city. In Herodotuss historically dubious account of Cyruss upbringing, Cyrus overthrows his grandfather Astyages and unites the latters Median kingdom with the Persian one he inherited. Cyrus, when he reached manhood in Persis, revolted against his maternal grandfather and overlord.



