We can even use them to predict the genotype and phenotype of future offspring, like in a married couple who wants to know the odds of one of their children having a particular disease. How do autosomal traits differ from sex-linked traits? What type of inheritance pattern could show a pedigree where a mother passes down a trait to all her children, sons and daughters?
Therefore all his sons will be unaffected, but his daughters may be carriers. These cookies do not store any personal information. Most pedigrees have a basic level of detail - they demonstrate who's married to who, who is deceased, and the number of progeny and their sex. One of the biggest hints suggesting X-linked dominant disorders is that a man who has an X-linked dominant disorder must pass it down to all his daughters, as that is the only chromosome he can give them.
Some forms of deafness are Y-linked. Test your knowledge with gamified quizzes. Galactosemia is an autosomal recessive disorder. 2). government site. Its 100% free. This is in contrast to autosomal recessive disorders that are said to "skip generations". What are common mistakes students make with sex linkage? Figure 5: X-linked recessive pedigree. Figure 8: Mitochondrial inheritance pedigree. Pedigree analysis is an analysis, examination, or demonstration of the inheritance pattern of particular trait(s) in human beings. 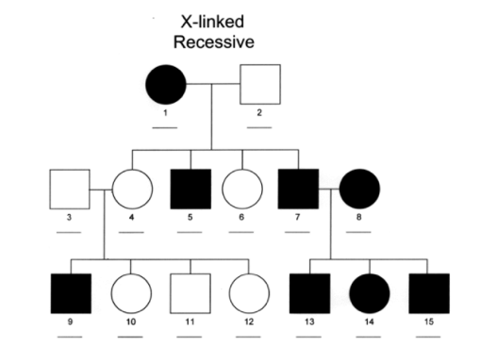 A chromosomal disorder where there are three copies of a chromosome instead of two. Two copies of the galactosemia allele are required to have the disease. Links to PubMed are also available for Selected References. Department of Medical Genetics, St. Mary's Hospital, Manchester.
A chromosomal disorder where there are three copies of a chromosome instead of two. Two copies of the galactosemia allele are required to have the disease. Links to PubMed are also available for Selected References. Department of Medical Genetics, St. Mary's Hospital, Manchester. 
 What is the main reason that gender-linked disorders are most often observed in males?
What is the main reason that gender-linked disorders are most often observed in males?
Young ID, Nugent Z, Grimm T. Autosomal recessive or sex linked recessive: a counselling dilemma. Generally, autosomal dominant disorders are present in every generation. These symptoms include vomiting, diarrhea, being really weak, and even cataracts due to excess galactose in the eyes. Those affected are typically marked in black, while those unaffected (considered the normal phenotype) have no coloring (or white). Learn more 8600 Rockville Pike Create flashcards in notes completely automatically. We'll assume you're ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Accessibility Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version.
Both mom and dad need at least one copy of this disorder for one of their children to have it. We see in Generation-I an affected man passes it on to three of his children- two daughters and one son. The discussion below considers only recessive traits. True or False: A man passes down an X-linked dominant trait to all his daughters. Definition of Pedigree Analysis in Biology, In the context of genetics, medicine, and biology, t, Regardless of their level of detail, pedigrees highlight who is affected by the disorder in question and who is not. Regardless of their level of detail, pedigrees highlight who is affected by the disorder in question and who is not. Characterization of dystrophin in muscle-biopsy specimens from patients with Duchenne's or Becker's muscular dystrophy. NCBI. That is not the inheritance pattern we see here, and this rules out the possibility that this trait, in this case galactosemia, is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern. People who have autosomal dominant disorders are typically __________. Chisom, Studysmarter. This website uses cookies to improve your experience. What tool can be used to look at the incidence of a disease in a family over several generations? None of those children are affected (draw this pedigree yourself to get some practice!). Figure 2: Galactosemia pedigree.
sharing sensitive information, make sure youre on a federal Which of these inheritance patterns is the rarest for genetic disorders? Create the most beautiful study materials using our templates. By registering you get free access to our website and app (available on desktop AND mobile) which will help you to super-charge your learning process. But what are the possible inheritance patterns we can see using pedigrees? What tricks would we use to classify the trait being studied in the pedigree as autosomal recessive? Because this is an autosomal recessive trait, carriers will not have the disease or any symptoms. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website. The above pedigree may seem very complex, but we can break it down to understand some basic principles. True or False: X-linked recessive disorders are much more common in boys. Thus, an affected woman passes down a trait to all her children, and only her daughters can pass it on to their children (Fig. Let's look at an unlabeled example to assess this (Fig. Before What kind of genes have an autosomal recessive pattern?
We will determine the answers to these questions with examples of each pedigree, of which there are six in Mendelian genetics. These references are in PubMed.
What is the name of the disorder that causes severe respiratory illnesses, is very common in North European individuals, and is due to a defect in chloride channels? X-linked dominant (the mother would have to have this disorder to pass it down to her son).
Before female relatives can be counselled, the probabilities of each mode of inheritance must be assessed, taking into account the prior probabilities, the pedigree structure, any DNA probe data, and any carrier testing data.
they are distinguished through notation - a sex-linked pedigree will have mostly affected males, the female carriers are typically designated as a half shaded circle. Thus, we can rule out: Let us look further up this pedigree, at the first generation. Texas Dept of State. We know the basic structures of pedigrees, the meaning of their symbols, and that they are used in genetics to study inheritance patterns. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. Identify your study strength and weaknesses. Galactosemia is a disorder of galactose accumulation in the blood due to a defect in the enzyme that metabolizes it. Looking at the youngest generation (generations are often labelled, with the oldest generation being I, their descendants being II, and the youngest being III), we can see there is a male child who is affected by galactosemia. Well, because an autosomal recessive trait must have two alleles in order for it to appear in the phenotype of an individual, thus the chances of suffering from a recessive trait are lower than those of suffering from a dominant trait. official website and that any information you provide is encrypted Because it is exclusively seen in males, we can safely presume the disorder is X-linked recessive. Grimm T. Genetic counseling in Becker type X-linked muscular dystrophy. Firstly, all affected individuals are males and they are inheriting this disorder from parents, both of which are not affected. What is the name of the tool/method that allows us to visualize chromosomes to examine their size, number, and shape? What kind of inheritance pattern leads to a mother passing down her disorder to all her children, boys and girls? Figure 4: Autosomal Dominant pedigree. HHS Vulnerability Disclosure, Help She would have to have two copies of this allele to have the disease, because women have two X-chromosomes. This means that the parent who has the trait also has the disorder, and when they pass this trait down the children who receive it will be affected as well (Fig. The widely used linkage analysis package LINKAGE can be used to do the calculation, which is much simpler than the conventional Bayesian method. FOIA Fill in the blank: Autosomal recessive disorders typically _____ a generation, Fill in the blank: Autosomal dominant disorders are typically present in _____ generation. This may not be the complete list of references from this article. PMC legacy view By using common sense and some fundamental principles, we can analyze pedigrees for just about any trait - from black hair color to osteogenesis imperfecta to dimples. Look at parents and children's state to determine this. Hoffman EP, Fischbeck KH, Brown RH, Johnson M, Medori R, Loike JD, Harris JB, Waterston R, Brooke M, Specht L, et al. What is the inheritance pattern of Hemophilia? The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the Let's look at a pedigree with such a scenario (Fig. However, we cannot rule out X-linked recessive. I. Bethesda, MD 20894, Web Policies Autosomal dominant traits are one of the easiest to recognize on pedigrees because every person exhibiting the trait has at least one parent exhibiting the trait. Families in which a single male is affected with a disease which might be either X linked recessive or autosomal recessive present problems in counselling. How many mutated chromosomes does a girl need to have this disorder? An official website of the United States government. We can then use them to determine the genotypes of existing family members. II: Practical considerations. Out of these, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website.
What ethnic background has a higher incidence of Tay Sachs Disease? will also be available for a limited time. Pedigrees are some of the most fun and exciting tools we have in inheritance studies. Very few disorders or traits have been discovered to be Y-linked. To solve a pedigree analysis, we must first determine if the trait is dominant or recessive. Earn points, unlock badges and level up while studying. 7). Now that we know the six major groupings of pedigree analysis, we can develop a problem sheet - in the form of a table- to help us consolidate the principles of each pedigree (Table 1). In fact, the preponderance of disorders that primarily affect men is typically due to the presence of a single X-chromosome, such that whatever disordered trait is on that chromosome cannot be masked by the normal trait that would be on a paired X-chromosome in females. Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Most genetic disorders are inherited in which pattern? Thus, that son is homozygous for the normal allele, and the affected individuals are all heterozygous for this trait. This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. We see there is another person affected with this trait in this family, in Generation-I. 3). National Library of Medicine Some pedigrees are more detailed, perhaps demonstrating the cause of death for those deceased, or adopted vs biological children. How many autosomes do human cells contain? How can we know that this disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion? Which is most common; X-linked dominant disorders, X-linked recessive, or Y-linked? Forrest SM, Smith TJ, Cross GS, Read AP, Thomas NS, Mountford RC, Harper PS, Geirsson RT, Davies KE. Let us consider the scenario in which the trait this woman has is X-linked recessive. The The new PMC design is here! Google Sites. Theoretical considerations. Figure 1: Typical pedigree symbols.
His offspring will get their mitochondria from their mother. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. If this disorder had an autosomal recessive inheritance, it would be seen in both male and female descendants. What kind of inheritance pattern does sickle cell anemia have? Autosomal traits can also be identified when a female offspring shows a recessive trait and the father is not affected & if an affected mother has a non-affected son.
The first and most common inheritance pattern that can be analyzed by pedigree is that of the autosomal recessive trait. What if we were look at a pedigree analysis of galactosemia (or any other autosomal recessive trait), but it was not labelled as such? Figure 6: X-linked dominant pedigree. What ethnic background has a higher incidence of sickle cell anemia? Pedigree analysis is important because it helps us to predict the likelihood of future offspring having a disorder. StudySmarter is commited to creating, free, high quality explainations, opening education to all. Rett Syndrome is an X-linked dominant disorder. Will you pass the quiz? This build-up of galactose can be toxic to certain tissues of the body. We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. Galactose is present in lactose, which is present in milk, so the first symptoms of galactosemia usually appear in the first couple days of life, after the new baby drinks formula or breast milk. In a pedigree displaying autosomal trait, affected individuals are of both sex: that is both male and female individuals could be affected in 1:1 ratio.
Galactosemia: galacto - referring to galactose, a sugar, semia - in the blood. We can see that neither his sisters nor his parents have galactosemia. Create beautiful notes faster than ever before. An autosomal trait generally appears to affect individuals in every generation.
Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM. Chegg.
Stop procrastinating with our study reminders. Create and find flashcards in record time. Analyze a pedigree by first determining the dominance of a trait, and then determining its sex-linkage. What is an example of linkage (organism, chromosome number, genes)? Those affected are typically marked in black, while those unaffected (considered the normal. True or False: A man passes down an X-linked dominant trait to all his sons. And which traits have which kind of particular inheritance pattern? of the users don't pass the Pedigree Analysis quiz! Modern genetics and neuromuscular disorders. How many copies of the hemophilia mutation do girls need to have the disorder? Let's say this is a pedigree of a family with Huntington's, a disease that causes problems with movement, neurological and psychiatric problems, often resulting in premature death. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. The site is secure. In case of autosomal trait, both male and female individuals could be carriers. Khan Academy. Wolff G, Mller CR, Grimm T. Benign muscular dystrophy: risk calculation in families with consanguinity.
So she would only have the disordered allele to give to her children, and while her daughters would get a normal X-chromosome from their father, all her sons would get an affected X-chromosome from her and a normal Y-chromosome from their father, and thus would have to be affected as well. All four of their children in Generation-II would be carriers. This creates three classes of individuals when it comes to an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance: those who have the disease (homozygous recessive), those who are carriers (heterozygous), and those who are neither (homozygous dominant). Everything you need for your studies in one place. Have all your study materials in one place. If a father has a disease and passes it down to all his daughters, but none of his sons, what is the inheritance pattern of this disease? Upload unlimited documents and save them online. Most X-linked disorders are recessive, but a few are dominant.
5). In the context of genetics, medicine, and biology, these traits are typically diseases and disorders. X-linked recessive disorders are passed from a woman (who is typically a heterozygote carrier) to both her sons and daughters. A woman with an X-linked dominant disorder passes it down to her sons and daughters equally. 50020 views What two tools are used frequently to test for the presence of trisomy in a fetus while they're still in utero? Why thankfully?
may see unaffected parents have affected offspring, both unaffected parents with affected offspring must be heterozygotes, these traits tend to skip a generation or two, unaffected parents cannot have affected offspring, any affected parents (almost always) are heterozygotes, these traits are present in every generation, any affected daughter must have an affected father, if passed down by mother: males and females equally affected, if passed down by father: only females affected, occurs in all male progeny of an affected father, occurs in all children of an affected mother, regardless of gender, affected sons cannot pass this down to their children, Pedigrees are typically used in the setting of, The most common inheritance patterns include, Some other less common inheritance patterns include. This is a simple pedigree, but we can see that this heterozygous couple (genotypes Gg) had one child with galactosemia, and three children with the normal phenotype. Figure 3: Autosomal recessive pedigree. The typical denotations in the pedigree analysis are seen below (Fig. about navigating our updated article layout. Learning how to analyze them requires pattern recognition and deductive reasoning, but these learning processes are not complicated since they are visual. If a man happens to have an X-linked recessive disorder, he cannot pass it down to his sons, whom he must pass his Y chromosome down to. Each affected person in Generation-II passes the disorder on to at least one of their children, and the Generation-II son who did not inherit the disorder, and did get married, did not pass it on to any of his four children. Chegg. However, all her sons will have the trait of the disorder, and her daughters (assuming her husband has the normal genotype) will either be carriers or homozygous for the normal allele (Fig. around the world. 8). Galactosemia can be passed down from mother to sons, or mother to daughters, or father to sons, or father to daughters. Because mitochondria are maternally inherited. Let's use the disease galactosemia to study this. Grimm T. Genetic counseling in Becker type X-linked muscular dystrophy. Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (524K), or click on a page image below to browse page by page. Sign up to highlight and take notes.
Set individual study goals and earn points reaching them.
(Fig. The .gov means its official. Wapenaar MC, Kievits T, Hart KA, Abbs S, Blonden LA, den Dunnen JT, Grootscholten PM, Bakker E, Verellen-Dumoulin C, Bobrow M, et al. 4). Why can't a male with a mitochondrially inherited disorder pass it down to his offspring?`. autosomal dominant (at least one parent would have to have the disorder to pass it down), Y-linked (the father must pass this down, so he would have the disorder), mitochondrial (a mother passes this down to. A pedigree analysis is a visual depiction of the genetic states of members of a family - carriers, affected, or completely unaffected. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. Free and expert-verified textbook solutions. Mitochondrial inheritance is maternal, meaning we get our mitochondria from our mothers. Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. Think of pedigrees as a family tree, but instead of perhaps going into detail about ethnic backgrounds or country of origin, pedigrees describe who has, who doesn't have, and who carries a genetic disorder (or multiple disorders!). Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly.
Ott J. Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. 1). If a woman has an autosomal recessive allele, and her husband has the same allele, but both of them have the normal phenotype, what is the probability that one of their offspring has the recessive phenotype? Best study tips and tricks for your exams. Pedigrees easily demonstrate the phenotypes of the individuals being studied. A deletion hot spot in the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience. Effective strategy for prenatal prediction of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. And an affected male must pass the trait down to all his sons. Pedigree analysis is visualized with a chart or diagram that maps out all relevant members of a family and exactly how they are related to one another. Chorionic Villus Sampling and Amniocentesis. What is the inheritance pattern for this disease? Read AP, Mountford RC, Forrest SM, Kenwrick SJ, Davies KE, Harris R. Patterns of exon deletions in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy. and transmitted securely. Thankfully, most genetic diseases! This explains how the woman in Generation-II, who married a random man who perhaps was a carrier as well, gave rise to an affected offspring. This affected woman gave birth to two sons, and two daughters. Michigan Genetics. Careers. Table 1: Hints for pedigree analysis problem sheets. Ultimately, we can know Y-linked traits because they never occur in females, only in males (Fig. what is the importance of pedigree analysis. Be perfectly prepared on time with an individual plan. Stop procrastinating with our smart planner features. 6). Now, if this affected woman in Generation-I has an autosomal recessive trait, then her genotype must include two copies of the affected allele (gg) and she would once again be able to distribute only this to her offspring, However, if their father has a homozygous healthy genotype, GG (which is typically assumed), then all their progeny would have the Gg heterozygous genotype.



